
Metal generates heat due to electromagnetic induction because of two main effects: Joule heating and magnetic hysteresis.
Joule heating is the result of electric currents flowing through the resistance of the metal. When a metal is subjected to an alternating electromagnetic field, it induces eddy currents within the metal. These currents are circular and flow in planes perpendicular to the magnetic field. The eddy currents encounter the resistance of the metal, which causes them to dissipate power in the form of heat.
Magnetic hysteresis is the result of the alignment of the magnetic domains of the metal. When a metal is subjected to an alternating electromagnetic field, it causes the magnetic domains of the metal to switch their orientation repeatedly. This switching process involves some energy loss, which is also dissipated as heat. Magnetic hysteresis is more significant in ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials, such as iron than in other metals.
The amount of heat generated by electromagnetic induction depends on several factors, such as the frequency and strength of the electromagnetic field, the electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability of the metal, the shape and size of the metal, and the coupling between the metal and the inductor.
Metal electromagnetic induction heating applicatiopns:

Induction Brazing (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Brazing? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=io3fURkB0WE Induction brazing is using alternating magnetic field – electromagnetic induction phenomenon, the eddy current effect in the magnetic field heats the workpiece,

Induction Melting (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction melting? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kyGyJAh667s The induction melting furnace is based on the electromagnetic induction heating principle to work, through electromagnetic induction to generate heat, the heating

Induction Forging (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction forging? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=78B3X_PQrX0 The core principle of induction forging furnace is to convert power frequency 50HZ AC to medium frequency (300HZ-20khz). The three-phase alternating current

Induction Hardening (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Hardening? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4R0me_Blhic Induction hardening is a quenching method that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to make the workpiece cut magnetic field lines in

Induction Annealing (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction annealing? Get A Quote Induction annealing is a part of induction heating. The purpose of induction annealing is to change the metal material’s hardness, toughness, and internal stress

Induction Tempering (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction tempering? Get A Quote For the whole induction hardening workpiece, especially the induction through heating hardening workpiece, the application of induction heating tempering is more convenient to form

Induction Preheating (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction preheating? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fbv71WNJj5I The welding of important components, alloy steel, and thick parts requires induction preheating before welding. The process means of heating the whole
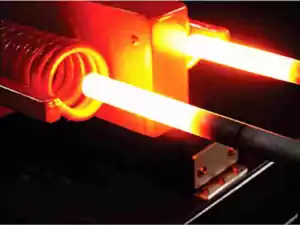
Induction Heat Treating (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Heat Treating? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u-CtIa-iejc Surface induction heat treatment in which the workpiece is heated locally by induction current. This induction heat treating process is often
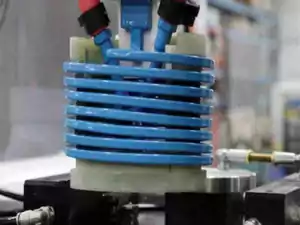
Induction Shrink Fitting (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Shrink Fitting? Get A Quote When the induction shrink fitting machine is working, The flux generated by the induction heating coil passes through the magnet and the heated

Induction Stress Relieving (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Stress Relieving? Get A Quote To induction stress relieving, annealed casting, forging and welding parts produce internal stress due to each part’s different cooling speed during cooling. Internal

Induction Heating (with pictures, videos, applications)
What’s Induction Heating? Get A Quote https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bm70gMbeGKk Electromagnetic induction heating, or called induction heating, is a method of heating conductive materials such as metals. It is mainly used for
